10 Effective Exercises for Computer Users to Combat Sedentary Work
In today’s digital age, prolonged hours spent working on laptops and computers have become commonplace. However, this sedentary lifestyle can lead to various health issues such as back pain, eye strain, and poor posture. Incorporating simple exercises into your daily routine can significantly alleviate these problems and enhance overall well-being.
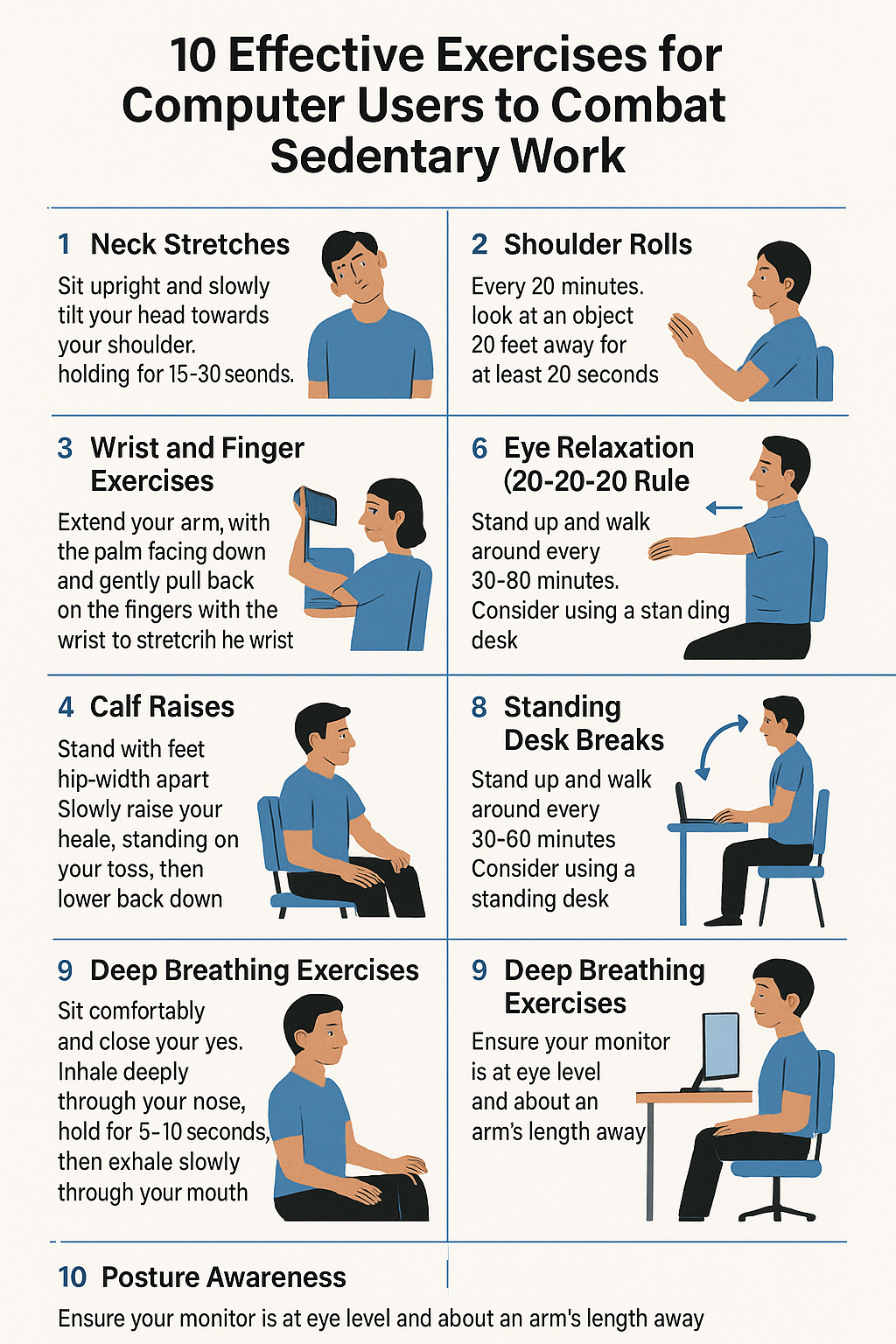
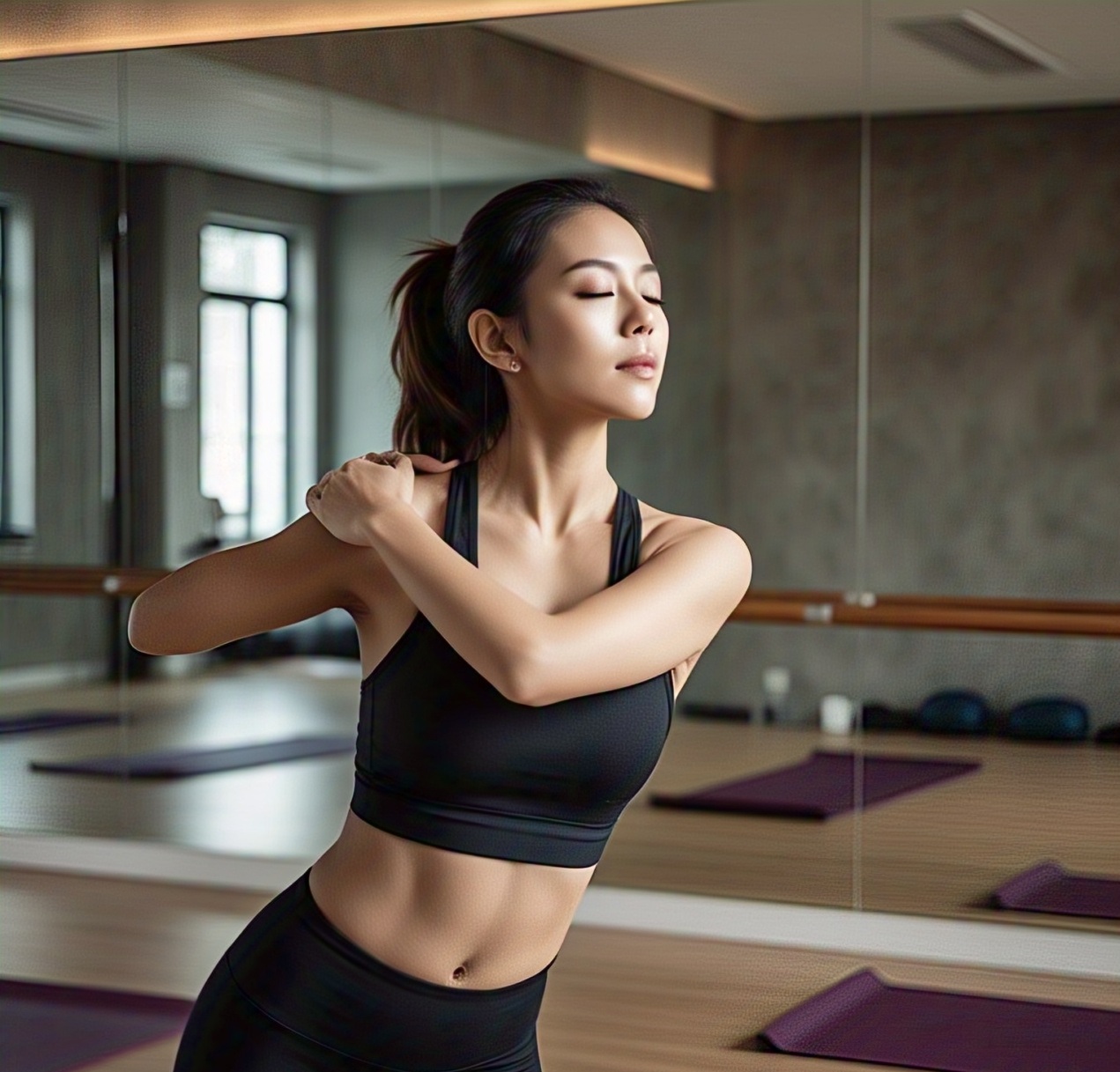
1. Neck Stretches

Extended screen time often results in neck stiffness and discomfort. To counteract this, perform gentle neck stretches
- Sit upright and slowly tilt your head towards your shoulder, holding for 15–30 seconds.
- Rotate your neck in a circular motion, first clockwise and then counterclockwise.
These stretches help in relieving tension and improving neck mobility.
2. Shoulder Rolls

Shoulder tension is a common issue among computer users. To alleviate this
- Sit or stand with a straight back.
- Roll your shoulders forward in a circular motion for 10–15 seconds.
- Reverse the direction and roll backward for another 10–15 seconds.
Regular shoulder rolls can reduce stiffness and enhance shoulder flexibility.
3. Wrist and Finger Exercises

Continuous typing and mouse usage can strain the wrists and fingers. To prevent discomfort
- Extend your arm with the palm facing down and gently pull back on the fingers with the opposite hand to stretch the wrist.
- Perform fist-to-fan exercises by making a fist, then spreading fingers wide apart, holding each position for a few seconds.
These exercises promote blood circulation and reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
4. Seated Spinal Twists

Prolonged sitting can lead to lower back stiffness. To alleviate this
- Sit upright with feet flat on the floor.
- Place your right hand on the outside of your left knee and gently twist your torso to the left, holding for 15–30 seconds.
- Repeat on the other side.
Spinal twists help in improving spinal flexibility and reducing lower back pain.
5. Eye Relaxation (20-20-20 Rule)

Staring at screens for extended periods can cause digital eye strain. To mitigate this:
- Every 20 minutes, look at an object 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds.
This practice helps in reducing eye fatigue and maintaining eye health.
6. Seated Leg Lifts

Sitting for long durations can weaken leg muscles. To strengthen them
- Sit upright with feet flat on the floor.
- Slowly extend one leg straight out and hold for 5–10 seconds.
- Lower the leg and repeat with the other leg.
Seated leg lifts enhance leg strength and promote better circulation.
7. Calf Raises

To improve lower leg strength and circulation:
- Stand with feet hip-width apart.
- Slowly raise your heels, standing on your toes, then lower back down.
- Repeat for 10–15 repetitions.
Calf raises help in strengthening calf muscles and improving blood flow.
8. Standing Desk Breaks

Prolonged sitting can lead to various health issues. To counteract this
- Stand up and walk around every 30–60 minutes.
- Consider using a standing desk to alternate between sitting and standing positions.
Regular movement helps in reducing the risks associated with prolonged sitting.
9. Deep Breathing Exercises

Stress can accumulate during work hours. To alleviate this:
- Sit comfortably and close your eyes.
- Inhale deeply through your nose, hold for a few seconds, then exhale slowly through your mouth.
- Repeat for 5–10 minutes.
Deep breathing exercises help in reducing stress and enhancing focus.
10. Posture Awareness

Maintaining proper posture is crucial for spinal health:
- Ensure your monitor is at eye level and about an arm’s length away.
- Sit with your back straight and shoulders relaxed.
- Keep your feet flat on the floor and knees at hip level.
Proper posture reduces the risk of musculoskeletal problems and enhances comfort during work.

Final Summary
Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can significantly improve comfort and reduce the adverse effects of prolonged computer use. Remember to take regular breaks, maintain proper posture, and stay active to promote overall health and well-being.







